Your shopping cart is empty!
Topic 1: What should know about 3D Printing?
- Khairul_Tajudin
- 10 Mar 2024
- Tutorial
- Beginner
- 199
Welcome to the exciting world of 3D printing! In this section, we'll embark on a journey to explore the fundamentals of 3D printing, a revolutionary technology that has transformed the way we create and manufacture objects.

This section will start with Introduction to 3D Printing. This topic is crucial for users with a foundational understanding of what 3D printing is and its various aspects.
1.1 What is 3D Printing?
At its core, 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a process that builds three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital model. This innovative technique enables the creation of intricate and customized objects with precision.
(Resource: pngitem)
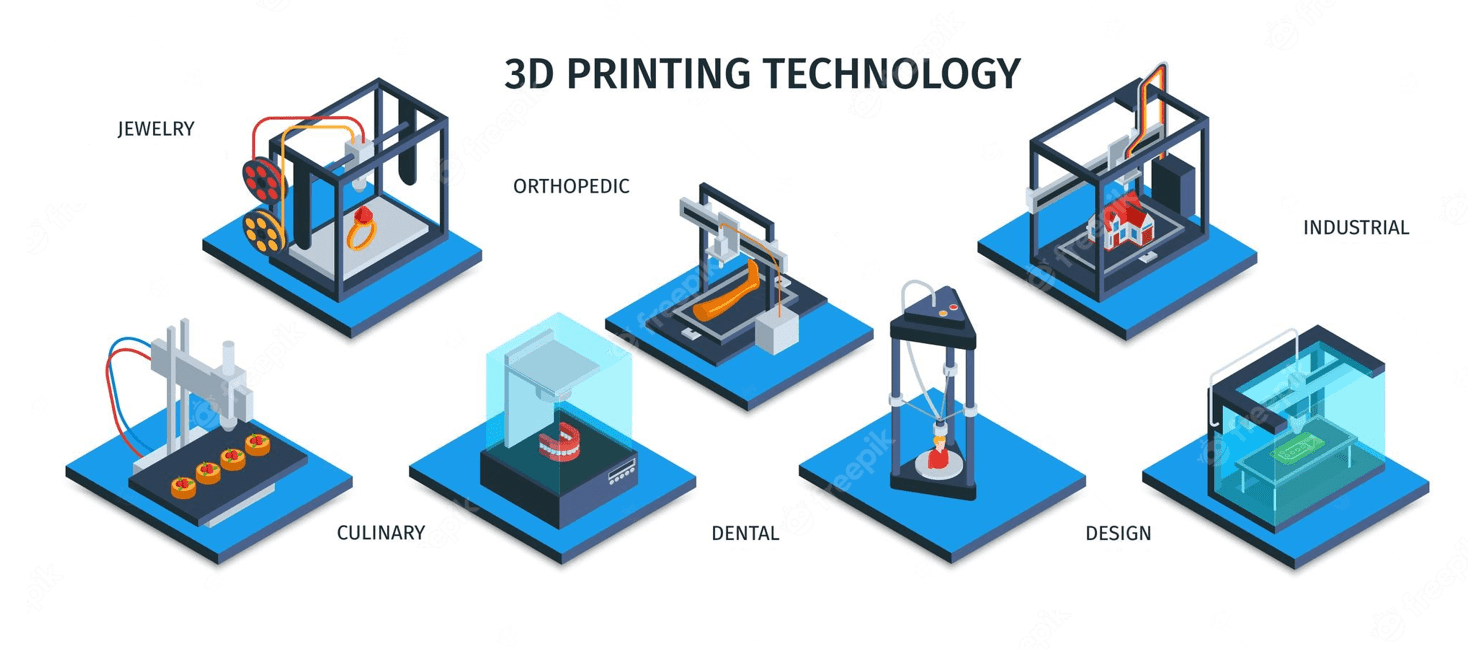
1.2 Applications of 3D Printing
Delve into the diverse applications of 3D printing across industries. From prototyping and product development to healthcare, architecture, and even food, 3D printing has proven to be a versatile tool with wide-ranging possibilities.
(Resource: 3DPrinterOS)
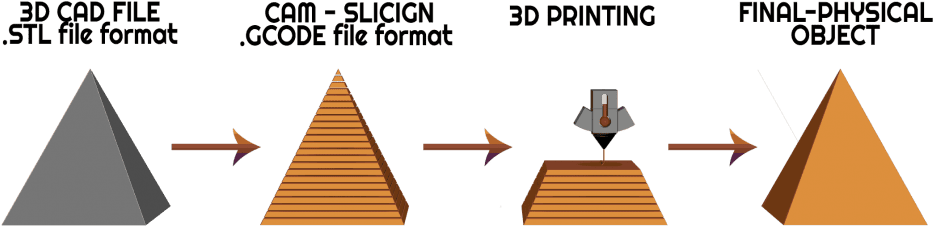
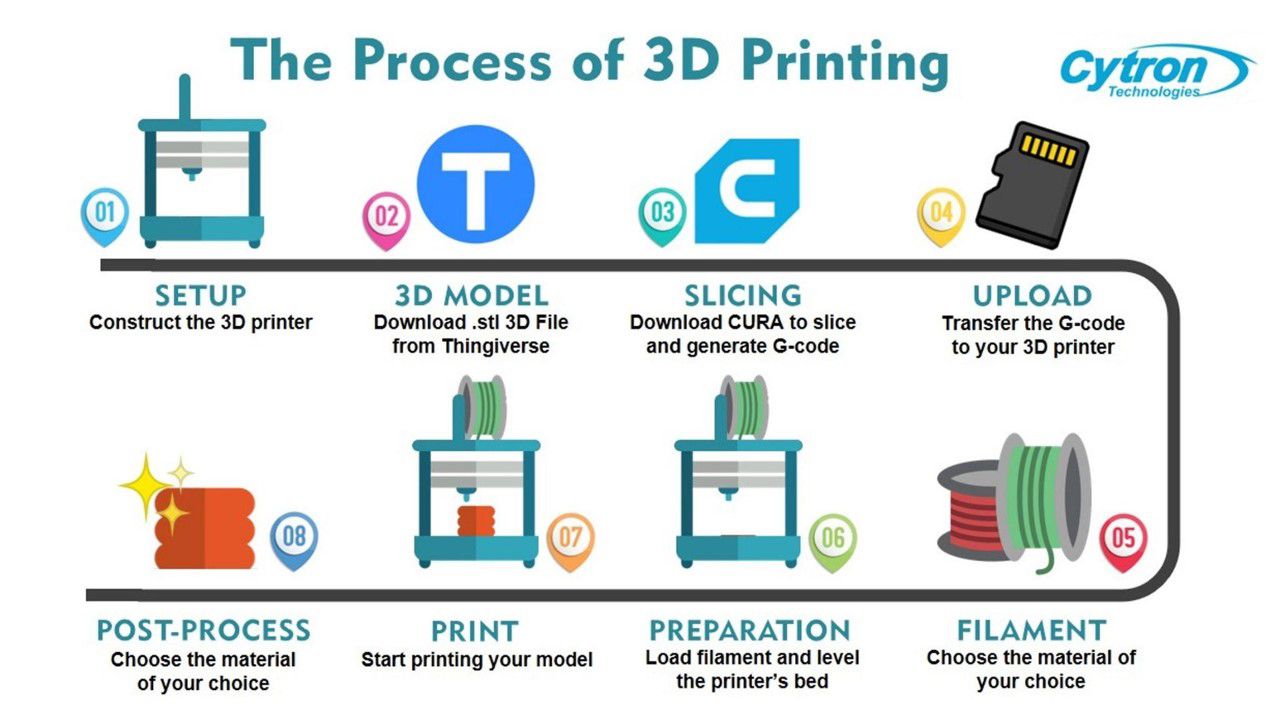
1.3 Understanding the 3D Printing Process
Explore the step-by-step process of how 3D printing works. This involves converting digital 3D models into physical objects through the deposition of material layer by layer. Key components, such as the printer, filament, and slicing software, play crucial roles in this intricate process.
1.4 Types of 3D Printers
Introduce the main types of 3D printers, including
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
Each type has its own set of strengths and is suitable for different applications.
1.4.1 Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM also known as fused filament fabrication (FFF), is an additive manufacturing (AM) process within the realm of material extrusion. FDM builds parts layer by layer by selectively depositing melted material in a predetermined path. It uses thermoplastic polymers that come in filaments to form the final physical objects.
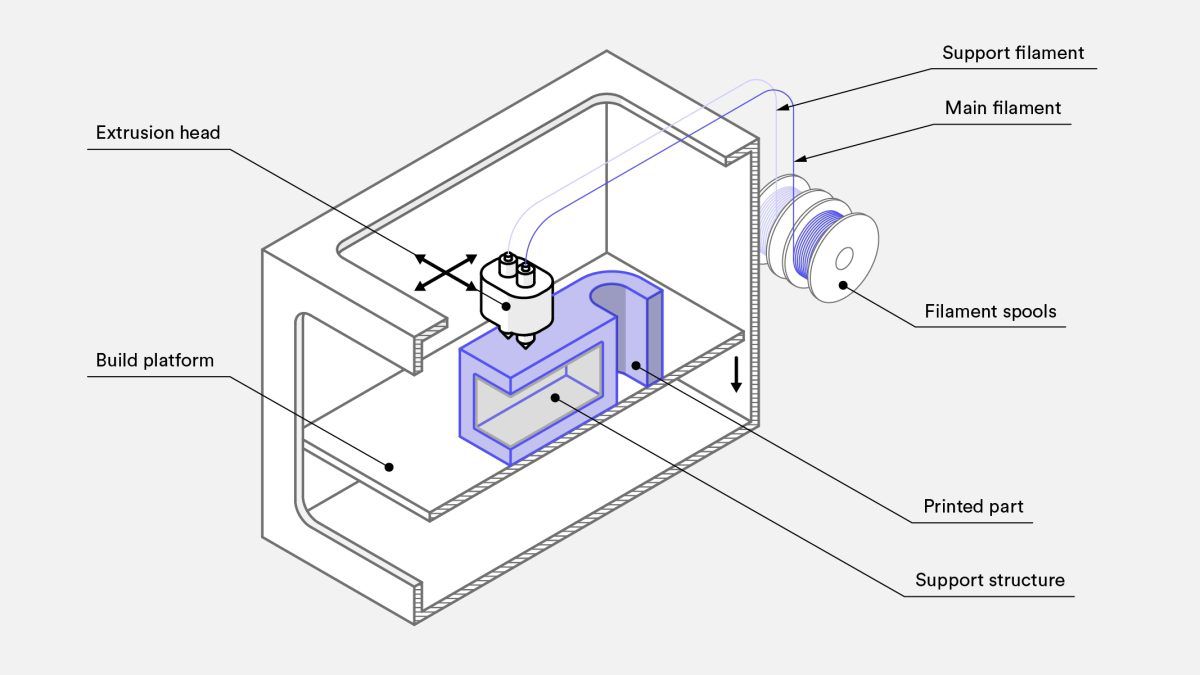
(Resource: hubs.com)
Characteristics:
- Melts and extrudes thermoplastic filament
- Lowest price of entry and materials
- Lowest resolution and accuracy
BEST FOR:
Basic proof-of-concept models and simple prototyping
1.4.2 Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA is the process owes its esteem in the additive space to its ability to produce prototypes that are accurate, isotropic and watertight, as well as production parts with impressive surface smoothness and more detailed features.
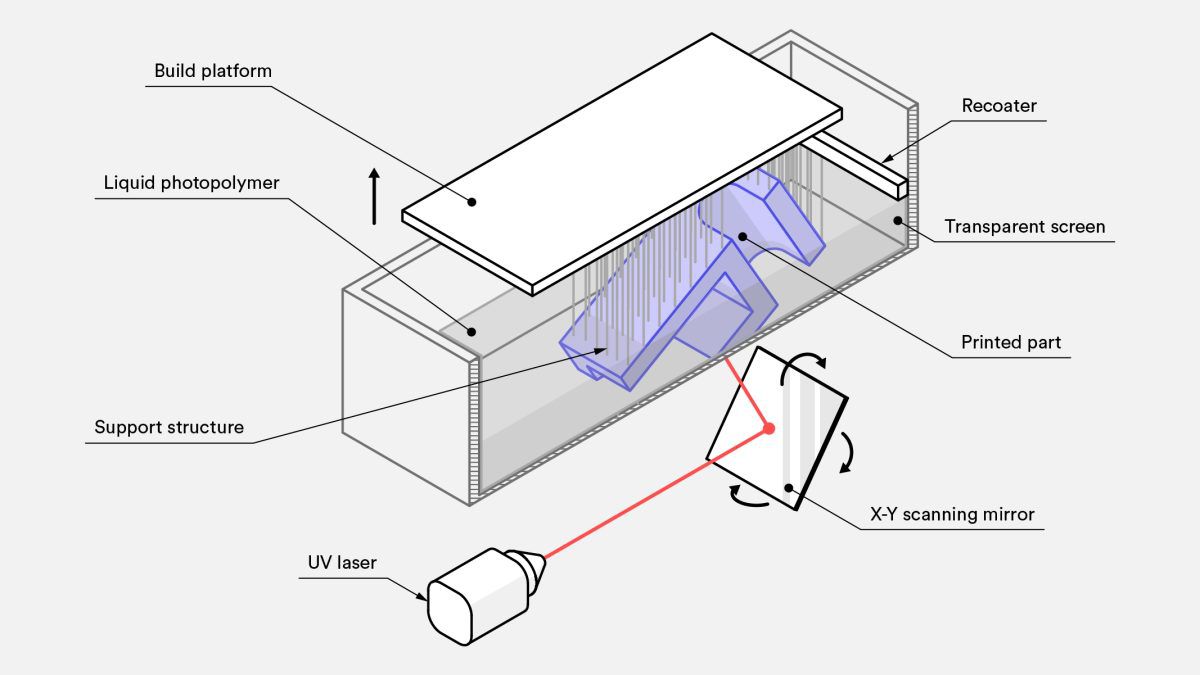
(Resource: hubs.com)
Characteristics:
- Laser cures photopolymer resin . Highly versatile material selection
- Highest resolution and accuracy, fine details
BEST FOR:
Functional prototyping, patterns, molds and tooling
1.4.3 Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS is an additive manufacturing process that belongs to the powder bed fusion family. In SLS 3D printing, a laser selectively sinters the particles of a polymer powder, fusing them together and building a part, layer by layer. The materials used in SLS are thermoplastic polymers that come in a granular form.
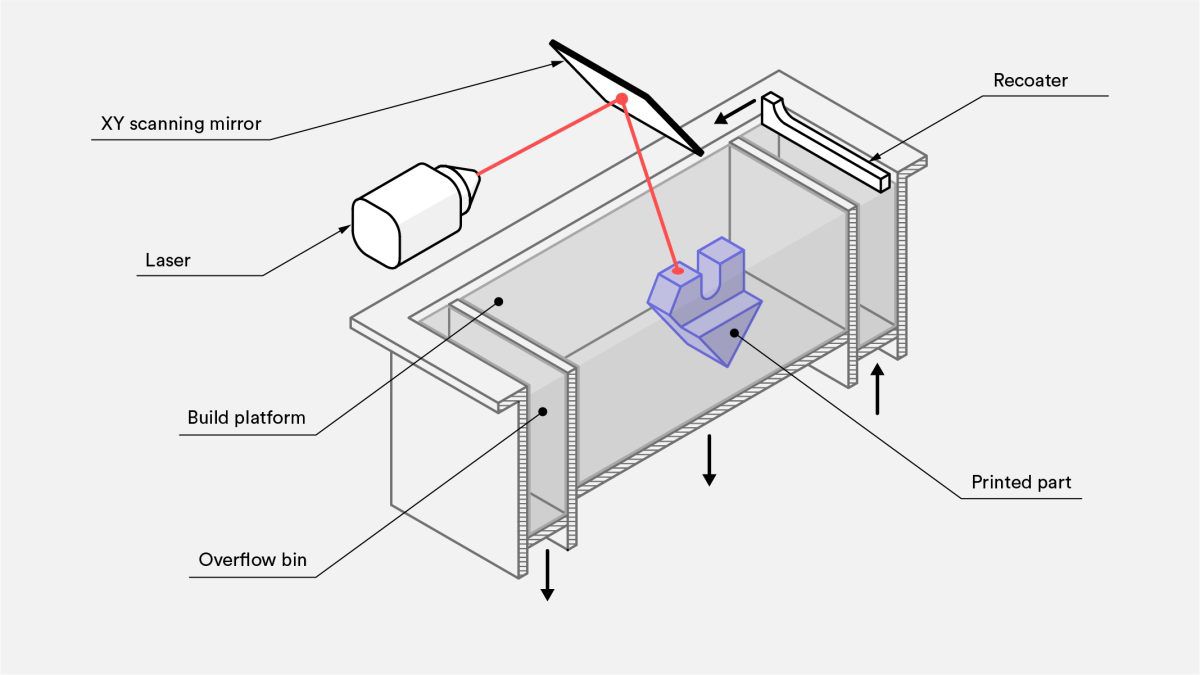
(Resource: hubs.com)
Characteristics:
- Laser fuses polymer powder
- Low cost per part, high productivity, and no support structures
- Excellent mechanical properties resembling injection-molded parts
BEST FOR:
Functional prototyping and end-use production
By the end of this section, you'll have a solid understanding of the basics of 3D printing, setting the stage for an immersive exploration of the technology's practical aspects in the subsequent sections. Let's dive in!
New to 3D Printing but not sure where to start?
You can start by being a part of our 3D Printing Community!
Hardware Components
Creality Ender-3 V3 SE 3D Printer + 1KG PLA
S$356.07 S$382.86 S$356.07
 International
International Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam

